Labral Tears
Hip Labral Tear
The hip labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of your hip joint. It serves several crucial functions, including joint lubrication, shock absorption, and hip stability. You can think of it as a seal that keeps the joint fluid in place, holding all the parts of your hip joint together.
After careful diagnosis, orthopedic specialists from the American Hip Institute can prescribe several effective treatment options for a hip labral tear. However, it is crucial to understand the various factors that can lead to the tearing of this supportive cartilage structure.
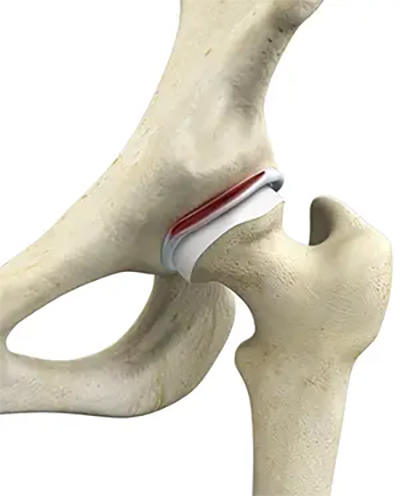
What Is a Hip Labral Tear?
A hip labral tear refers to an injury to or degeneration of the labrum, the ring of cartilage surrounding the outer edge of your hip joint socket. Patients with this condition can experience several distinct symptoms. However, other patients may not exhibit symptoms and may continue their daily activities without noticing any problem with their hips.
The treatment options provided by our team at the American Hip Institute are customized to the patient's needs. Our certified health professionals recommend treatments depending on the severity of the tear, the associated symptoms, and the patient's overall condition. Initial treatments may include non-invasive techniques, including rest, activity modification, and physical therapy. However, in more severe cases, our specialists may recommend surgery.
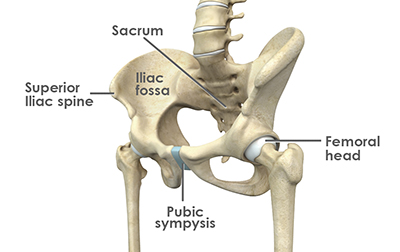
Understanding the Anatomy of the Hip Joint
To better understand what a labral tear in the hip is, it is helpful to review how the hip joint works. The hip is a ball-and-socket joint, where the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket, and the head of the femur (thigh bone) forms the ball.
These two structures comprise the two main parts of the hip joint. During any motion, like walking or running, the femoral head rotates and glides within the socket, which allows for a wide range of motion. The labrum acts like a cushion, protecting both of these bones from wear and tear.
Thus, a hip labral tear refers to the damage to this ring of cartilage between the ball and socket of your hip joint. When this structure is damaged or torn, it can cause inflammation and impact the nerves in the hip joint, causing one to experience pain and other symptoms. The disruption of the hip’s suction seal also causes the joint to lose its lubrication and stability, compromising the articular cartilage and potentially accelerating the progression of arthritis.

Symptoms of Hip Labral Tears
Patients with a torn labrum may be symptomatic or asymptomatic. However, if you experience any of the symptoms below, it may indicate a torn labrum:
- Pain in the groin area
- Pain in the lower back or buttocks
- Weakness and instability in the hip joint
- Catching or locking sensations
- Clicking sounds
- Limited range of motion
- Stiffness in the hip
After reviewing the symptoms that may point to a tear of the labrum, certified medical professionals from the American Hip Institute can perform further tests to confirm the diagnosis.

Causes of Hip Labral Tears
Some people may be more susceptible to tearing their labrum due to their hip anatomy or genetics. Specific activities that result in the overuse of the hip joint can also put you at risk. A torn labrum can be due to several causes, including:
- Structural abnormalities that place additional stress on the labrum, often involving hip impingement
- Degenerative changes in the hip joint, often in older patients
- Frequent participation in high-impact activities that, over time, lead to joint wear and tear
- Repetitive movements performed during certain exercises or daily activities
- Traumatic injuries, such as motor vehicle accidents or sports injuries, commonly from football, soccer, basketball, and snow skiing
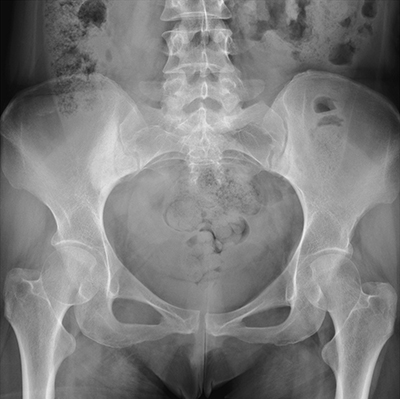
Diagnosis of Hip Labral Tears
Diagnosing a torn labrum in the hip can involve a combination of a medical history review, assessment of symptoms, physical examination, and imaging tests. Our providers at the American Hip Institute may utilize any of the following tests to diagnose your condition:
- X-Rays: Providers can rule out other possible underlying conditions that may contribute to the pain you're experiencing. Using X-rays, they can check for structural abnormalities and fractures.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): This imaging test can be used to evaluate the condition of your labrum and other soft-tissue structures. An MR arthrogram (MRA) is an imaging procedure that involves injecting a contrast dye material into the hip joint space to clearly visualize the labrum and other structures.
- Physical Examination: Various physical examination maneuvers can test range of motion, joint stability, and pain with specific tests that are sensitive to labral tears or other conditions of the hip. These tests include the flexion / adduction / internal rotation (FADIR) impingement test, which is highly sensitive to labral tears.
- Medical History: Our certified medical practitioners will also inquire about your medical history, including previous injuries and surgeries, in conjunction with your current symptoms.
- Diagnostic Injection With Local Anesthetic: In some cases, a diagnostic injection using a local anesthetic may be administered into the joint space to determine whether a patient’s pain is stemming from damage to structures within the hip joint, like the labrum, or from elsewhere.

Treatment Options for Hip Labral Tears
Treatments for hip labral tears vary depending on the severity of the tear, the patient's symptoms, and individual needs and preferences. Patients with a minor labral tear may recover within a few weeks with the help of non-surgical treatments.
Here are some of the conservative treatment options available to you at the American Hip Institute:
- Activity Modification and Rest: Doctors may recommend avoiding certain activities and opting for rest to help reduce symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help improve your range of motion and strengthen the muscles supporting your hip joint.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce the pain and inflammation associated with torn cartilage.
Surgery for Hip Labral Tears
Doctors can recommend surgery, such as hip arthroscopy, when non-invasive conservative treatments do not provide relief. This minimally invasive procedure requires only two to three small incisions in the hip joint area and the insertion of a camera called an arthroscope to visualize the labrum.
Depending on the severity of the tear, the surgeon may either repair the labrum or reconstruct it using a graft. In the case of smaller tears, the torn labrum can be reattached to the socket using sutures and anchors and the surrounding area cleaned up. For larger, irreparable tears, the surgeon can remove the native labrum and replace it with a graft that provides the same function. This restores the native anatomy of the hip and the suction seal of the joint. If any bony deformities are present and causing impingement, those can be corrected during the procedure as well.

Post-Operative Care
Following the surgery, you will be given instructions on caring for your incisions, activities to avoid, and exercises to perform for a fast recovery and successful outcome. The use of crutches and a hip brace will be necessary for some time, depending on the procedure that was performed, to protect the newly repaired or reconstructed labrum. Physical therapy in the following months will help you restore strength and mobility. Your surgeon will also prescribe pain medications to keep you comfortable during this time.

Work With Leading Hip Experts
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, you may have suffered a hip labral tear. Experts from the American Hip Institute can provide personalized minimally invasive treatments, treating the injury and addressing the root cause. Our team uses cutting-edge therapies to diagnose and resolve your injury quickly so you can get back on your feet in no time. Contact us today to schedule a consultation.
